Stairway Safety: Decoding Handrail Regulations
Ever gracefully ascended a staircase, hand gliding effortlessly along a sturdy handrail? It's a seemingly simple act, yet behind that smooth ascent lies a complex web of building codes and regulations designed to ensure safety and accessibility. These "codes for handrails on stairs," as they're formally known, are more than just suggestions; they are crucial guidelines that dictate everything from handrail height and placement to materials and load-bearing capacity.
Understanding these regulations is vital for architects, builders, homeowners, and anyone involved in the design, construction, or renovation of stairways. Ignoring these guidelines can lead to safety hazards, accessibility issues, and even legal ramifications. This deep dive will unravel the intricacies of handrail codes, exploring their historical development, practical implications, and the critical role they play in ensuring safe and accessible environments for everyone.
Handrail regulations, while seemingly modern, have roots stretching back centuries. Early building practices, though less formalized, often included handrails out of necessity. As buildings grew taller and stairways more complex, the need for standardized safety measures became increasingly apparent. Over time, these evolved into the codified regulations we see today, constantly being refined to reflect advancements in building technology and a growing understanding of human factors like ergonomics and accessibility needs.
The core purpose of these regulations is straightforward: to prevent falls and ensure safe navigation of stairways. They address critical safety concerns by specifying minimum handrail heights, ensuring adequate grasping space, and dictating the structural integrity of the handrails themselves. This standardized approach minimizes the risk of accidents, offering protection to everyone from young children to elderly individuals with mobility challenges.
However, navigating these regulations can be complex. Variances exist between international, national, and even local building codes, often leading to confusion. Interpreting these codes accurately and applying them correctly is essential to ensure compliance and, more importantly, to guarantee the safety and accessibility of stairways. This exploration aims to clarify these complexities, providing a clearer understanding of handrail regulations and their practical implications.
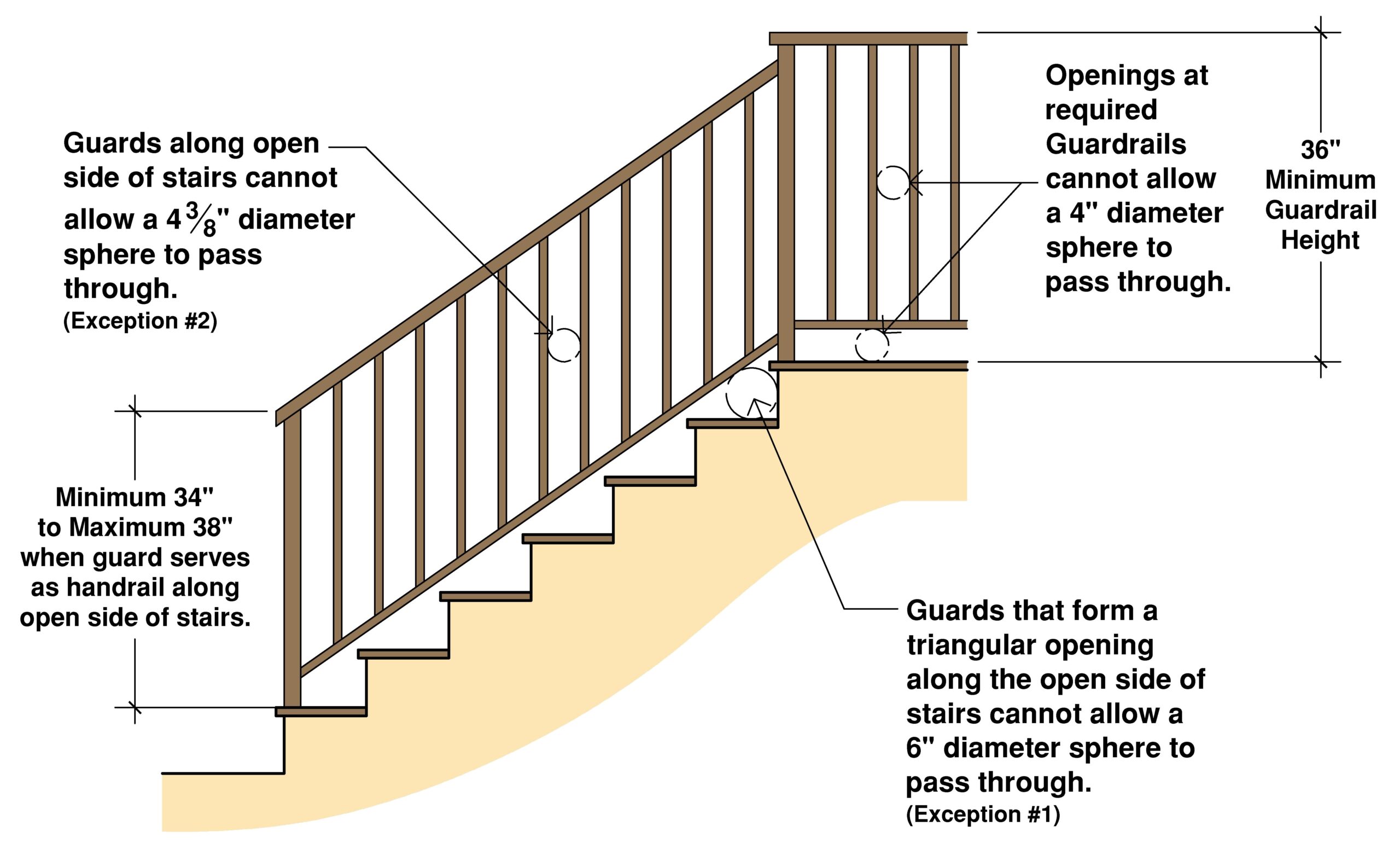
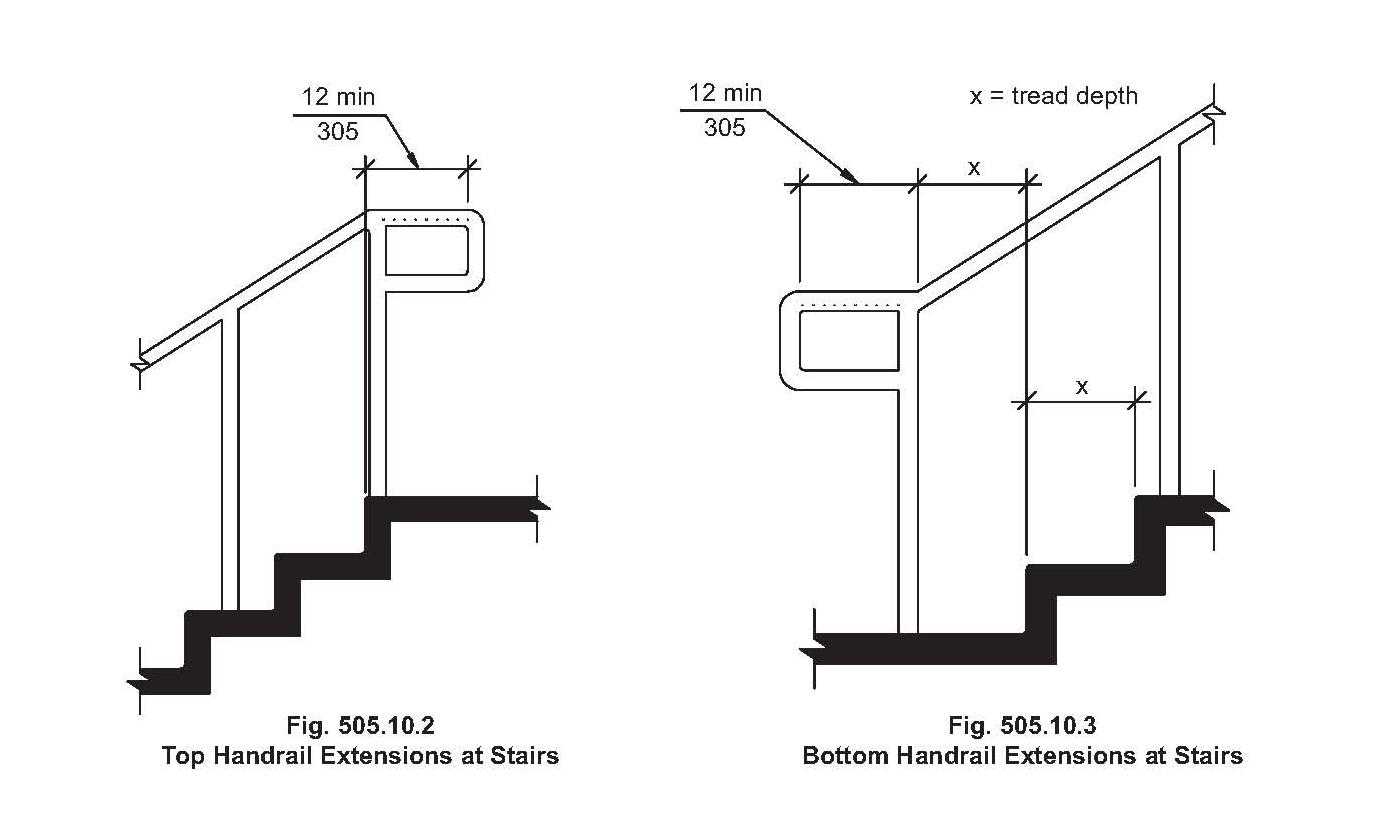
While specific regulations vary, common elements include height requirements (typically between 34 and 38 inches), specifications for handrail diameter and shape for comfortable gripping, and requirements for continuous handrails along the entire length of the stair flight. Regulations also address handrail extensions beyond the top and bottom risers, ensuring safe transitions onto and off of the stairs.
Benefits of adhering to handrail codes are threefold: enhanced safety, improved accessibility, and legal compliance. By following these guidelines, you create safer environments, reducing the risk of falls. You also ensure accessibility for people with disabilities, promoting inclusivity. Finally, compliance with building codes protects you from potential legal issues and liabilities.
An action plan for ensuring handrail compliance starts with research. Identify the specific codes applicable to your location and project. Consult with building inspectors or accessibility experts for clarification. Then, meticulously plan your stairway design, ensuring all elements meet the required specifications. Finally, document everything, keeping records of materials used, measurements taken, and inspections conducted.
A checklist can include items like verifying handrail height, checking for continuous runs without interruptions, ensuring proper clearance between the handrail and the wall, and confirming the structural integrity of the handrail and its mounting hardware.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Safety | Potential Increased Costs |
| Improved Accessibility | Complexity of Regulations |
| Legal Compliance | Potential Design Limitations |
Best Practices: 1. Consult local codes. 2. Use durable materials. 3. Ensure proper installation. 4. Conduct regular inspections. 5. Consider user needs.
FAQs: What is the standard handrail height? What materials are acceptable for handrails? Are handrails required on both sides of the stairs? ...
In conclusion, handrail regulations are essential for creating safe and accessible stairways. From their historical roots to their modern-day applications, these codes play a vital role in protecting individuals from falls and ensuring inclusivity. By understanding and adhering to these regulations, we can create environments that prioritize safety, accessibility, and well-being. Take the time to research applicable codes, consult with experts, and prioritize the implementation of proper handrails. Your diligence will contribute to safer and more accessible spaces for everyone.
Unlocking the potential of the taki framework
Navigating bankruptcy crucial questions for your attorney
Unlocking hidden knowledge