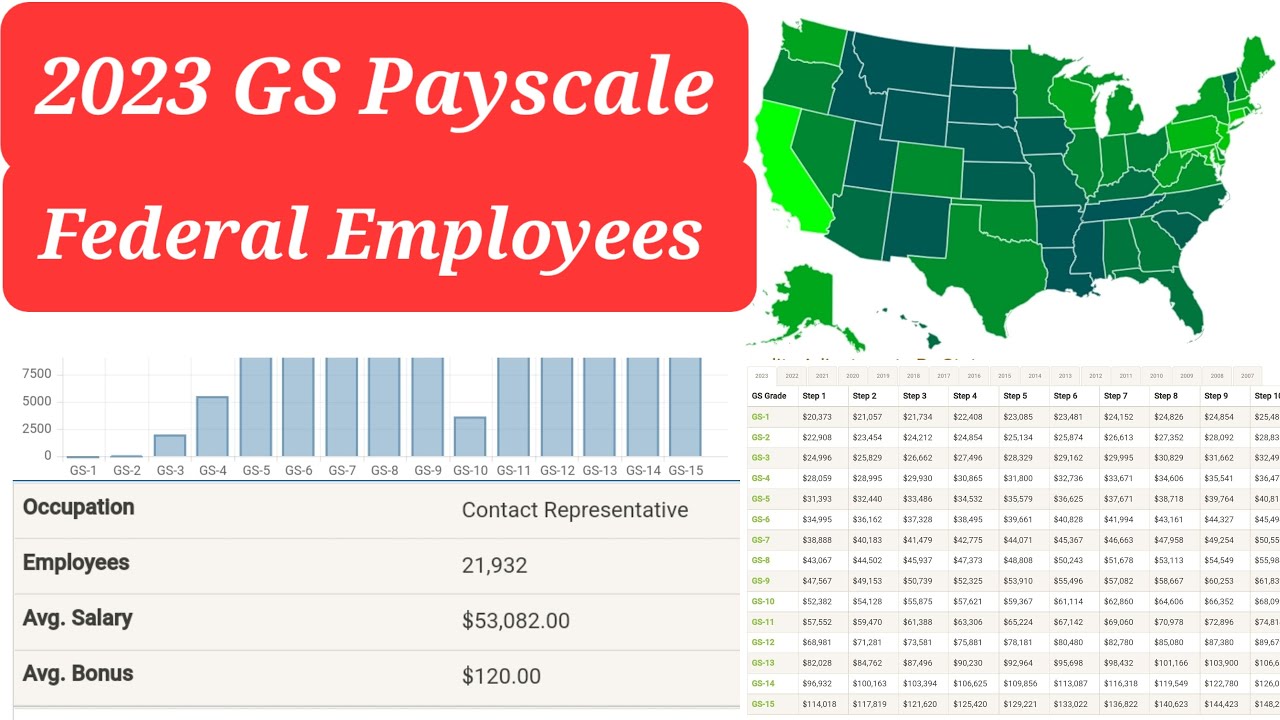
GS 9 Step 9 to GS 11: Your Guide to Career Advancement
Are you a GS 9 employee at Step 9, looking towards the next step in your federal career? The journey from GS 9 Step 9 to GS 11 is a significant leap, marking not just a salary increase, but also increased responsibility and a higher level of contribution. This transition requires strategic planning, dedicated effort, and a thorough understanding of the process. This article provides a comprehensive guide to navigating this crucial career advancement.
Moving from a GS 9 Step 9 to a GS 11 isn't merely a matter of time served. It involves demonstrating a readiness to take on more complex tasks, showcasing leadership potential, and actively pursuing opportunities for professional growth. This involves understanding the specific requirements of the GS 11 position you're targeting and aligning your skills and experience accordingly.
The federal government's General Schedule (GS) pay system classifies positions based on the level of difficulty, responsibility, and required qualifications. Each GS level comprises multiple steps, representing incremental salary increases within that level. Reaching Step 9 of GS 9 typically represents the maximum earning potential within that grade. Therefore, progressing to GS 11 is often the next logical step for career advancement and increased earning potential.
The origins of the GS system can be traced back to the Classification Act of 1923, aimed at standardizing federal positions and pay. Over the years, this system has evolved, but the core principle of classifying jobs based on complexity and responsibility remains. Understanding the history and evolution of the GS system provides context for the importance of progressing through the grades, such as the move from GS 9 to GS 11.
One of the main issues associated with moving from GS 9 Step 9 to GS 11 is the competition. Many qualified GS 9 employees aspire to reach the GS 11 level, making the selection process highly competitive. This necessitates a proactive approach, not just meeting the minimum requirements, but exceeding them and actively showcasing your capabilities and potential.
A key aspect of successfully transitioning to a GS 11 role is understanding the specific requirements of the target position. Review vacancy announcements carefully, paying attention to the knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) required. Tailor your resume and application materials to highlight how your experience and qualifications directly address these KSAs.
Three key benefits of attaining a GS 11 position include increased salary, greater responsibility, and enhanced career opportunities. The higher salary offers improved financial stability. Greater responsibility translates to more challenging and fulfilling work, contributing to professional growth. Finally, reaching the GS 11 level opens doors to future leadership roles and further career advancement within the federal government.
Creating a clear action plan is essential. This should include identifying target GS 11 positions, networking with individuals in those roles, seeking mentorship, and participating in professional development opportunities to enhance your KSAs. Actively seeking feedback on your performance and identifying areas for improvement is crucial.
While specific examples of GS 9 Step 9 to GS 11 transitions vary depending on the agency and career field, the underlying principles remain consistent: demonstrate your readiness for increased responsibility, showcase your skills and abilities, and actively pursue opportunities for growth. Networking, mentorship, and continuous learning are vital components of a successful transition.
Frequently asked questions related to the GS 9 to GS 11 promotion often revolve around eligibility criteria, the application process, timelines, and tips for a successful application. Answers to these questions can usually be found on agency websites or by consulting with human resources personnel.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Moving to GS 11
Here's a simple breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages of making the leap to a GS 11 position.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Increased Salary | Increased Competition |
| Greater Responsibility | Higher Expectations |
| Enhanced Career Opportunities | More Demanding Workload |
In conclusion, the transition from GS 9 Step 9 to GS 11 is a significant step in a federal employee's career. It requires dedication, strategic planning, and a thorough understanding of the process. By proactively pursuing professional development opportunities, showcasing your skills and abilities, and networking with individuals in your desired field, you can significantly improve your chances of a successful promotion. This transition not only represents increased earning potential but also greater responsibility and a more impactful contribution to the federal government. Embracing this journey with a clear action plan and a commitment to continuous learning is key to achieving your career goals and making a lasting impact within your agency.
Boat switch panels mastering your maritime electrical system
Unmasking the trickster a deep dive into deception and subversion
Navigating pennsylvania state employee salary growth