Decoding the GS Pay Scale
Navigating the labyrinthine world of federal employment can be daunting. One crucial element often shrouded in mystery is the General Schedule (GS) pay scale. This system determines the salaries of the vast majority of white-collar federal employees, from entry-level analysts to seasoned scientists. Understanding this structure is essential for anyone considering or currently navigating a career within the federal government.
The GS pay scale isn't just a static list of numbers; it's a dynamic framework influenced by locality, grade, and step. Each grade represents a different level of responsibility and complexity, while each step within a grade signifies progression and experience. Locality pay adjustments further tailor salaries to reflect the cost of living in different geographic areas. This complex interplay of factors can make understanding a GS pay scale document seem like deciphering a complex code.
The origin of the GS pay system can be traced back to the Classification Act of 1923, which aimed to standardize and regulate federal positions and salaries. This act laid the foundation for a more equitable and transparent compensation system, moving away from the often arbitrary and inconsistent practices of the past. Over the years, the GS system has undergone numerous revisions and adjustments, reflecting changes in the economic landscape and the evolving needs of the federal workforce.
Accessing reliable and up-to-date information on the GS pay scale is crucial. While a "GS pay scale PDF" might seem like a convenient resource, relying solely on downloaded documents can be risky. Official government websites, such as the Office of Personnel Management (OPM), offer dynamic online tools that provide the most current and accurate information. These resources often include interactive calculators and comprehensive explanations, making it easier to understand how your salary is determined.
One of the primary challenges associated with the GS pay scale is its perceived rigidity. Some argue that the structured nature of the system can limit flexibility and hinder recruitment and retention of top talent, especially in highly competitive fields. However, the system provides a framework for consistent and fair compensation across the federal government. The GS system also ensures equal pay for equal work, preventing salary discrepancies based on factors such as gender or race.
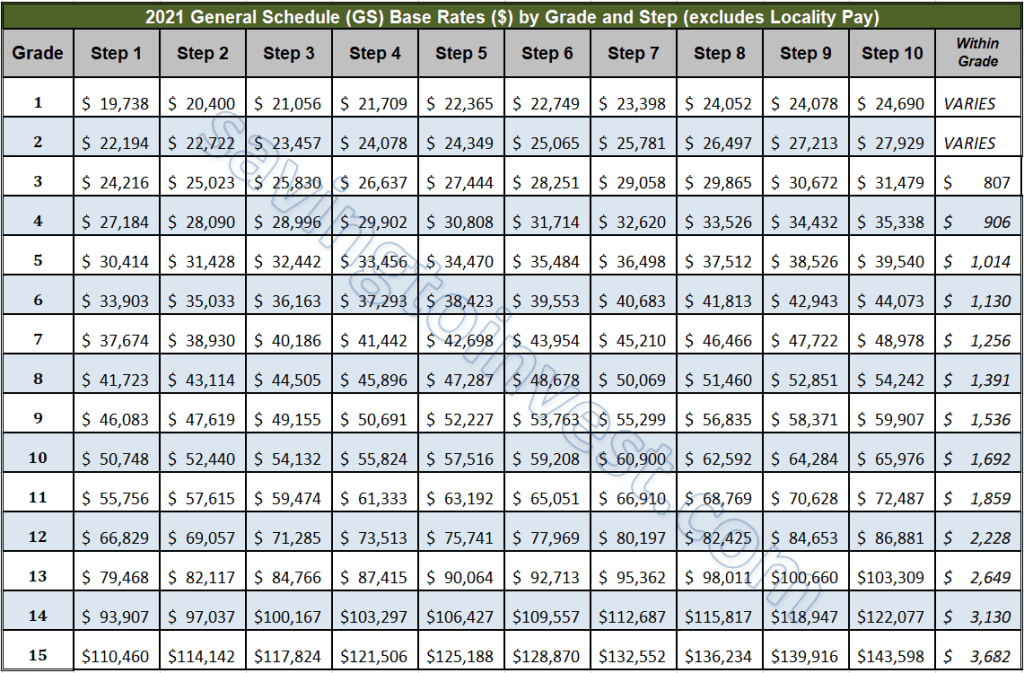
The GS pay scale consists of 15 grades, ranging from GS-1 to GS-15. Each grade is further divided into 10 steps, representing incremental increases within that grade. To determine your potential salary, you need to identify your grade and step, as well as your locality pay area. The OPM website provides a wealth of resources, including pay tables and calculators, to assist in this process.
Benefits of understanding the GS pay scale include informed career planning, accurate salary expectations, and effective negotiation during the hiring process. For example, knowing the salary range for your target position allows you to assess whether the offered compensation aligns with your financial goals and market value. It also empowers you to advocate for yourself during salary negotiations.
If you're aiming for a federal career, research available positions and their associated GS grades. Utilize the OPM's online resources to determine salary ranges. During the interview process, don't hesitate to discuss salary expectations based on your qualifications and the GS pay scale.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Pay Scale
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency and Consistency | Potential Rigidity |
| Equal Pay for Equal Work | Difficulty Attracting Specialized Talent |
Five best practices for navigating the GS system: 1) Regularly consult the OPM website for updates. 2) Understand your locality pay area. 3) Research potential career paths and their corresponding GS grades. 4) Utilize online salary calculators to estimate your potential earnings. 5) Advocate for yourself during salary negotiations.
Frequently Asked Questions: 1) How is locality pay determined? 2) What is a step increase? 3) How can I advance within the GS system? 4) What are the benefits of federal employment? 5) How do I find federal job openings? 6) What qualifications are required for different GS grades? 7) How does the GS system compare to private sector compensation? 8) What are the different types of pay adjustments?
Tips and Tricks: Use online resources like the OPM salary calculator. Network with current federal employees. Stay informed about changes to the GS system. Negotiate your salary based on your experience and qualifications.
In conclusion, the GS pay scale, often presented as a dense "GS pay scale PDF," is a complex yet crucial element of federal employment. Understanding its intricacies, from grade and step to locality pay, is paramount for anyone navigating this career landscape. By leveraging online resources, staying informed about updates, and advocating for yourself, you can effectively navigate the GS system and ensure fair compensation for your valuable contributions. Don't let the complexity intimidate you – empower yourself with knowledge and unlock the potential of a fulfilling federal career.
Conquering the ap physics c mechanics frq beast
Unlocking the secrets of the forbidden books index
Fallen in love meme ya me enamore meme explained