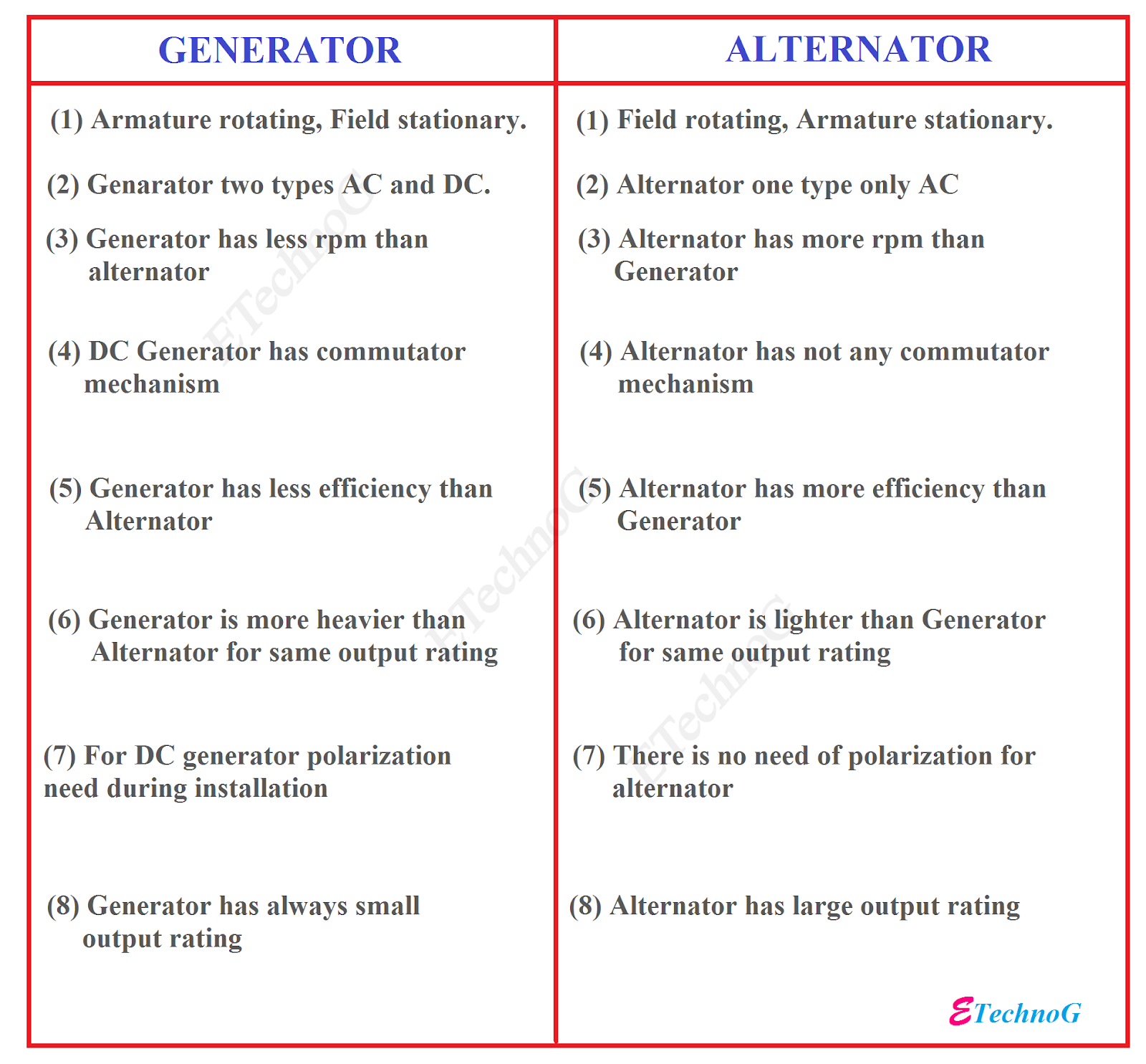
AC vs. DC: Unlocking the Electrical Current Mystery
Ever wondered about the electricity that powers our homes and devices? It's not all the same. The electrical current that flows through our wires comes in two main forms: alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Understanding the difference between AC and DC voltage is fundamental to grasping the electrical world around us.
The distinction between AC and DC isn't just a technicality; it affects everything from the design of power grids to the type of batteries we use. This seemingly simple difference has shaped the development of modern technology and continues to influence our energy future.
One of the easiest ways to visualize the difference is to think of water flow. DC voltage is like a river flowing steadily in one direction. AC voltage, on the other hand, is like the tide, constantly changing direction, pushing and pulling the current back and forth.
This fundamental difference arises from how the electricity is generated. DC electricity is produced by sources like batteries and solar cells, which maintain a constant voltage polarity. AC electricity, however, is generated by rotating generators, which cause the voltage to alternate cyclically.
Historically, the "War of the Currents" in the late 19th century pitted Thomas Edison, a proponent of DC, against George Westinghouse and Nikola Tesla, who championed AC. Ultimately, AC triumphed due to its ability to be easily transformed to higher or lower voltages, making it more efficient for long-distance transmission.
DC power's constant voltage is ideal for electronic devices and charging batteries. AC's ability to be transformed makes it the preferred choice for power transmission over long distances. Understanding this distinction is key to appreciating the complexities of our electrical infrastructure.
A simple example of DC voltage at work is your flashlight. The batteries provide a constant stream of electrons in one direction, powering the bulb. Your household outlets, on the other hand, supply AC voltage, where the direction of electron flow changes many times per second.
One benefit of understanding the AC/DC difference is choosing the correct power supply for your electronics. Another is understanding why certain appliances, like motors, can run on either AC or DC, while others, like computers, require DC. Lastly, this knowledge enables you to appreciate the engineering marvel of our electrical grid, which efficiently delivers power over vast distances.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AC and DC
| Feature | AC | DC |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Transformation | Easy | Difficult |
| Long-Distance Transmission | Efficient | Inefficient |
| Safety | Lower at high voltage | Higher at lower voltage |
| Electronic Device Compatibility | Requires conversion to DC | Directly compatible |
Best Practices for Working with AC and DC:
1. Always ensure you are using the correct voltage and current type for your device.
2. Never touch exposed wires carrying AC or DC current.
3. When working with high voltage, use appropriate safety equipment.
4. Consult a qualified electrician for any electrical work beyond basic tasks.
5. Understand the specific requirements of AC and DC circuits before undertaking any projects.
Real-world Examples:
1. Power Transmission Lines (AC)
2. Laptop Chargers (AC to DC conversion)
3. Solar Panels (DC)
4. Electric Vehicle Batteries (DC)
5. Household Appliances (Mostly AC)
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What's the main difference between AC and DC? AC changes direction periodically, while DC flows consistently in one direction.
2. Why is AC used for power transmission? It can be easily transformed to high voltages, reducing transmission losses.
3. Why do electronics use DC? Electronic components require a stable, unidirectional current for proper operation.
4. Can I convert AC to DC? Yes, using devices called rectifiers.
5. Can I convert DC to AC? Yes, using devices called inverters.
6. Is AC or DC more dangerous? Both can be dangerous; the level of risk depends on the voltage and current.
7. What is the frequency of AC power? Commonly 50Hz or 60Hz.
8. What is the unit of measurement for voltage? Volts (V).
Tips and Tricks:
When dealing with electrical circuits, prioritize safety. Always double-check voltage and current ratings before connecting any devices.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between AC and DC voltage is crucial for anyone interacting with electrical systems. From the power grid that supplies our homes to the batteries that power our portable devices, AC and DC play distinct and essential roles. Recognizing their unique characteristics allows us to safely and effectively utilize electricity, powering the technologies that shape our modern world. By appreciating the historical significance of the "War of the Currents" and the ongoing advancements in electrical engineering, we can better prepare for a future driven by efficient and sustainable energy solutions. This understanding empowers us to make informed decisions about our energy consumption and contribute to a more electrified world. So, next time you plug in a device or flip a light switch, remember the fundamental difference between AC and DC, the two invisible forces that drive our technological advancements.
Umd spring semester endgame decoded
The art of physics cover pages printable designs and their impact
Harris county tx power outage map your guide